Steps of Scientific Inquiry or Method
Steps of Scientific Inquiry or Method
What is scientific inquiry or method?
The scientific inquiry or method is defined as a method of research in which a problem is identified, relevant data is gathered, a hypothesis is formulated from this data, and the hypothesis is empirically tested.
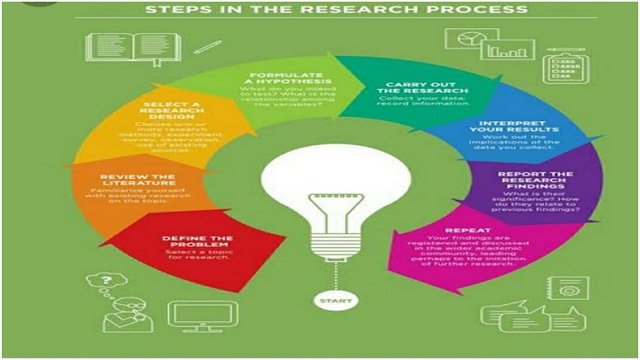
STEPS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY OR METHOD
There are various major steps included under scientific inquiry
1) Define the problem
2) Review the literature
3) Setting research, questions, objectives, and hypothesis
4) Choosing or selecting the study design
5) Formulate a hypothesis
6) Carry out the research/experimentation
7) Interpret your results
8) Report the research findings
1) Define the problem
Defining the problem is necessarily the first step of the research process. A person using the scientific method must first identify a problem that needs solving. Scientific research process seeks to address a problem. Defining problem will give purpose and direction to the research process.
For example, a scientist may be interested in knowing whether aspirin can cure baldness in men.
2) Review the literature
Scientific knowledge is not static, review helps scientists to understand how knowledge in a particular field is changing and developing over time.
Review of the literature provide-
-Provide a basic idea of the topic area
-Critically analyse a selected topic using a published body of knowledge
- Provide an indication of what further research is necessary
3) Setting research questions, objectives and hypothesis
Research objectives are to be first set to find out what we aim to achieve through our research. They are specific actions that you will take and act as milestones that will help you complete our research. Some of the research questions should developed within ourselves that will be specific concern that need to be answered through your our research.
4) Choosing or selecting the study design
A research design encompasses the methodology and procedure employed to conduct scientific research. Although procedures vary from one field of inquiry to another, identifiable features distinguish scientific inquiry from other methods of obtaining knowledge.
There are many ways to classify research designs, but some examples include descriptive (case studies, surveys), correlational (observational study), semi-experimental (field experiment), experimental (with random assignment), review, and meta-analytic, among others. Another distinction can be made between quantitative methods and qualitative methods.
5) Formulate a hypothesis
A hypothesis is an assumption or suggested explanation about how two or more variables are related. It is a crucial step in the scientific method and, therefore, a vital aspect of all scientific research. There are no definitive guidelines for the production of new hypotheses.
While there is no single way to develop a hypothesis, a useful hypothesis will use deductive reasoning to make predictions that can be experimentally assessed. If results contradict the predictions, then the hypothesis under examination is incorrect or incomplete and must be revised or abandoned. If results confirm the predictions, then the hypothesis might be correct but is still subject to further testing.
6) Carry out the research/experimentations
Research/Experimentations are carried out to test the hypothesis. Experiment tests whether your prediction is accurate and thus your hypothesis is supported or not. It is important for your experiment to be a fair test. You conduct a fair test by making sure that you change only one factor at a time while keeping all other conditions the same.
7) Interprets your results
Once your experiment is complete, you collect your measurements and analyze them to see if they support your hypothesis or not.
After experimentations if the predictions were not accurate and their hypothesis was not supported, in such cases communicate the results of the experiment and then go back and construct a new hypothesis and prediction based on the information we learned during our experiment. Even if we find that our hypothesis was supported, then it is necessary to test it again in a new way.
8) Report the research findings
The final step of scientific method is reporting the research findings. The findings are reported, shared and discussed in order to evaluate the results or conclusion for any potential errors in the procedure and determining a follow up question to find out more about the research



Comments
Post a Comment